Syzygy R&D roadmap
The Syzygy R&D roadmap calls for launching the platform commercially in 2023 and adding multiple additional product launches over the next few years. While this page doesn't include all long-term product planning, it discusses our priorities through the next several years. All products use the same Rigel photoreactor design with different designer photocatalysts and feedstocks to deliver the end product.
Hydrogen photoreactors
Our hydrogen photoreactors are currently undergoing field trials with expectations of full commercialization in 2023. We are capable of utilizing different feedstocks depending on customer requirements.
Photocatalytic decomposition of ammonia (P-DA)—2023
The P-DATM photoreactor has the potential to produce clean hydrogen from green ammonia and renewable electricity. It breaks ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen. This technology has real promise for producing zero-emissions hydrogen.
Photocatalytic steam-methane reforming (P-SMR)—2023
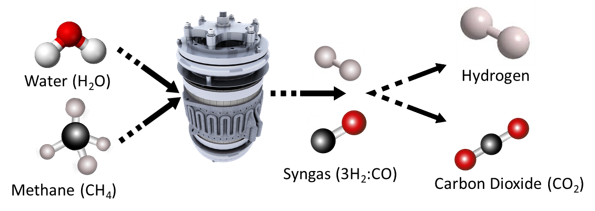
The P-SMRTM photoreactor is a low-emission alternative to traditional greenhouse-gas-heavy steam-methane reforming, which requires incredibly high temperatures (steam that is between 700 and 1,000°C) achieved by burning fossil fuels. Our P-SMR reactors use light instead of heat to combine methane and water molecules to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. This technology is a lower-carbon alternative that can be easily plugged into existing hydrogen plants.
Carbon dioxide utilization photoreactors—2024
We are on track to deliver CO2-to-XTM photoreactors in 2024. This technology combines carbon dioxide and methane to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which are integral to synfuel and methanol production. CO2-to-X technology gives us a solution for processing the CO2 collected in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) facilities into something useful. Instead of burying carbon dioxide and hoping for a future solution, this technology gives us a cost-effective way to use carbon dioxide to our benefit in the very near future.
Ammonia synthesis photoreactors (P-AS)—2025
P-ASTM photoreactors will use photocatalytic dry reforming to convert hydrogen and nitrogen to ammonia. P-AS reactors give us the ability to synthesize green ammonia from green hydrogen produced in regions with abundant renewable electricity. The ammonia can then be shipped anywhere in the world, especially to regions without the ability to produce renewable electricity. Green ammonia can be used as fuel, fertilizer, or split back into hydrogen and nitrogen for hydrogen fuel cells and other uses. Green ammonia provides a clean, efficient way to ship energy stores around the world and will be critical to the energy transition.
Ethylene Photoreactor
Future plans also include the development of an ethylene photoreactor to produce clean ethylene.